AQUA LIFE GUARD COMMERCIAL (1000 LPH)
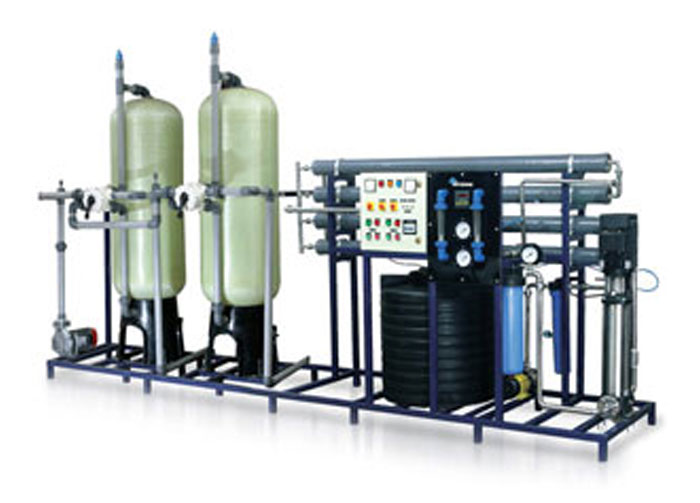

| S.No. | Particulars | Qty. |
|---|---|---|
1. |
Frame MS Coated |
1 |
2. |
Raw water pump CRI |
1 |
3. |
Multi Grade Filter 13 x 54 FRP Vessel |
1 |
4. |
Carbon Filter 13 x 54 FRP vessel |
1 |
5. |
10/5 Micron x 20” Pre filter Big Blue & Housing |
2 |
6. |
Antiscalant Dosing Pump with Dosing Tank of 100 Liter Tank. |
1 |
7. |
Membrane Pressure Vessel 4040 FRP Single element |
4 |
8. |
Membrane BW 4040 |
4 |
9. |
Pressure Gauge |
4 |
10. |
High Pressure Vertical RO Pump & Motor CRI |
1 |
11. |
1800 LPH Rota meter for Permeate |
1 |
12. |
2500 LPH Rota meter for Reject |
1 |
13. |
High Pressure & Low Pressure Switch Each |
1 |
14. |
On Line Starter. |
1 |
15. |
TDS Meter |
1 |
16. |
Dimensions : 5ftX3ftX4.5ft |
|
AQUA LIFE GUARD INSTITUTIONAL 50-75 LPH MODEL
Dimension |
||
Dimension in mm |
- |
|
Weight in kg |
- |
12 |
Price |
||
AQUA LIFE GUARD Institutional 50-75 LPH: Rs. 49,500/- |
||
Warranty |
||
|
||

Stage 1 – Water Softener Removes Hardness To Prevent the System From Scaling
Stage 2 SPUN Filter (5 Micron) This filter removes larger particles such as dust, sand and other suspended particles above 5 microns and therefore it renders clarity to incoming water.
Stage 3 - Sediment Filter The sediment filter is third step in the water purification process. This filter uses a 5 – 10 micron polypropylene-spun fiber filter to remove sediments and other impurities, upgrading the water quality one level and improving the performance and life of main membrane. This gives high clarity of water.
Stage 4 - Activated Carbon Filter
The carbon filter made from high grade silver impregnated carbon removes chlorine, organic impurities, color and odor from water. It also inhibits the growth of bacteria in the cartridge. This makes the water crisp to taste.
Stage 5 - Reverse Osmosis Membrane
Reverse osmosis membrane having pore size of 0.0001 micron retains all the contaminants like bacteria, viruses, pyrogen and toxic cancer causing chemicals like pesticides, VOCs, Trihalomethanes. The reverse osmosis membrane reduces 90 - 95 % of total dissolved salts, thereby imparts good taste to water. It also removes harmful chemicals like fluoride, arsenic and heavy metals. This makes the water pure, safe and crystal clear
Stage 6 – Post Carbon Cartridge
Improves Taste
AQUA LIFE GUARD WATER SOFTENER
Features Flow Rate : 0-1000 LPH
Electricity : 200W /Ac-220v/50Hz
Equipments : FRP Vessel, Auto Multiport Valve, Pressure Gauges, Feed Pump
Resin : Cation Exchange Resin (25Ltrs.)
Softening Capacity : Max. Hardness up to750ppm
Operating Mode : Automatic (Also available in manual system)
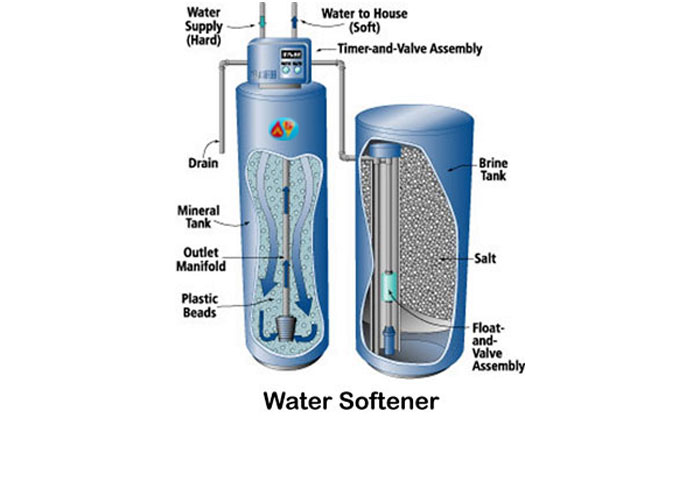
A water softener is a water treatment system that reduces the hardness in the water down to below one grain per gallon. In order to do this, chemicals such as salt are used in the treatment of the water. A salt-based water softener will provide brighter laundry using less soap and will prevent the buildup of scale around the shower. Many people love their water softeners for these exact reasons.
What is Hard Water?
Hard water is a buildup of minerals in the water supply. The buildup of minerals can plug up the pipes and wreak havoc on any water based appliances in the home, such as washing machines, dishwashers, faucets and other fixtures. The best way to remove hardness from the water is with a water softener
What are the advantages of a water softener?
There are numerous reasons why a water softener should be considered a prime investment in your home. The first and most important reason is the removal of hardness from your water. Hard water clogs the plumbing and any water based application that relies on the plumbing. With a water softener, you will no longer need to worry about an increase in energy bills, or expensive repair cost. A water softener will also increase the lifespan of your clothing, and keep them looking like they were shri and new. Soft water will leave a clean feeling on your skin after a shower or bath.
How Much do Water Softeners Cost?
Water softeners can be Vary from Rs 10000 to 1000000. Depending upon the Hardness and Requirement of Quantity. When it comes to a water softening system spending more money does not always mean you are getting a better product. AQUA LIFE GUARD offers the highest quality water softeners, complete with warranties and satisfaction guaranteed for fractions of the cost that big name manufactures charge, with home systems starting at under Rs 10,000/-
Does a water softener actually save money on soaps and detergents?
Consumers can cut back on dish and laundry detergent use by 50 percent or more and lower washing machine temperatures from hot to cold just by using softened water, as shown by two new independent studies that were recently released. By using softened water in washing machines, they can reduce detergent use by 50 percent and save energy by washing in 60ºF cold water instead of 100ºF hot water, achieving the same or better stain removal and whiter clothes compared to results in hard water.
In areas having very hard water, consumers can cut detergent use in dishwashers and washing machines by more than 50 percent after softening, and get the same results.
The results show that softened water might not only save consumers money but could also be environmentally friendly, because they can reduce reliance on polluting fuels because of energy savings and help cut back on harmful detergents going into water streams.
The laundry study looked at stain removal, putting into the machines from half to the entire amount of manufacturers’ recommended levels. Water hardness ranged from none to 30 grains per gallon, and wash temperature was 60, 80 and 100ºF. It was found that soft water is better at removing stains than increased water temperature or more detergent being used.
Notably, softened water with the least amount of detergent and lowest temperature actually provides a higher degree of whiteness compared to increased hardness and both high temperature and large amounts of detergent. This was found to be true for all stains and all the detergents tested.
“Better performance and savings can be achieved with softened water,” the report’s authors concluded.
Demineral Water Plant
AQUA LIFE GUARD RO System is a leading provider of deionization solutions. Our water deionizers are rugged, pre-engineered, pre-assembled, standardized units that minimize expensive installation and start-up costs. We have designed our Deionization systems to maximize the efficiency and repeatability of the unit during the service and regeneration modes .
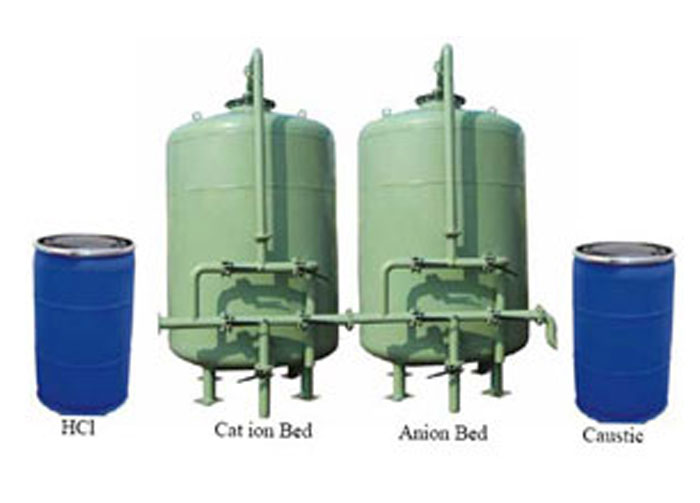

In the context of water purification, ion-exchange is a rapid and reversible process in which impurity ions present in the water are replaced by ions released by an ion-exchange resin. The impurity ions are taken up by the resin, which must be periodically regenerated to restore it to the original ionic form. (An ion is an atom or group of atoms with an electric charge. Positively-charged ions are called cations and are usually metals; negatively-charged ions are called anions and are usually non-metals).
The following ions are widely found in raw waters:
Ion Exchange ResinsThere are two basic types of resin - cation-exchange and anion-exchange resins. Cation exchange resins will release Hydrogen (H+) ions or other positively charged ions in exchange for impurity cations present in the water. Anion exchange resins will release hydroxyl (OH-) ions or other negatively charged ions in exchange for impurity anions present in the water.
The application of ion-exchange to water treatment and purification
There are three ways in which ion-exchange technology can be used in water treatment and purification: first, cation-exchange resins alone can be employed to soften water by base exchange; secondly, anion-exchange resins alone can be used for organic scavenging or nitrate removal; and thirdly, combinations of cation-exchange and anion-exchange resins can be used to remove virtually all the ionic impurities present in the feedwater, a process known as deionization. Water deionizers purification process results in water of exceptionally high quality.
DeionizationFor many laboratory and industrial applications, high-purity water which is essentially free from ionic contaminants is required. Water of this quality can be produced by deionization.The two most common types of deionization are:
- Two-bed deionization
- Mixed-bed deionization
The two-bed deionizer consists of two vessels - one containing a cation-exchange resin in the hydrogen (H+) form and the other containing an anion resin in the hydroxyl (OH-) form. Water flows through the cation column, whereupon all the cations are exchanged for hydrogen ions. To keep the water electrically balanced, for every monovalent cation, e.g. Na+, one hydrogen ion is exchanged and for every divalent cation, e.g. Ca2+, or Mg2+, two hydrogen ions are exchanged. The same principle applies when considering anion-exchange. The decationised water then flows through the anion column. This time, all the negatively charged ions are exchanged for hydroxide ions which then combine with the hydrogen ions to form water (H2O).
Cations |
Anions |
Calcium (Ca2+) |
Chloride (Cl-) |
Magnesium (Mg2+) |
Bicarbonate (HCO3-) |
Sodium (Na+) |
Nitrate (NO3-) |
Potassium (K+) |
Carbonate (CO32-) |
Iron (Fe2+) |
Sulfate (SO42-) |
Technical Specifications: |
||||||
Model No. |
DM-10 |
DM-20 |
DM-30 |
DM-50 |
DM-65 |
|
Material of construction |
FRP |
FRP |
FRP |
FRP |
FRP |
|
Flow rate LPH |
Max |
100 |
200 |
600 |
1000 |
1500 |
Min |
10 |
20 |
60 |
100 |
150 |
|
Working Pressure Kg/CM2 |
Max |
2.5 |
2.5 |
2.5 |
2.5 |
2.5 |
Min |
0.5 |
1.5 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
Qty. of Ion exchange resin Lits. |
10 |
20 |
30 |
50 |
65 |
|
Output regeneration in Lits. |
200 |
600 |
1000 |
1750 |
2200 |
|
(Base on 1000 PPM IDS in Haw Water) |
||||||
Regenerate |
|||||
Commercial grade HCL |
Kg |
2.5 |
6 |
10 |
16 20 |
Caustic flakes (NaOH) |
Kg |
0.5 |
1.2 |
2.2 |
4.0 5.0 |
Treated Water Quality |
|||||
Electrical Conductivity Micromhos / Cm |
< 30 |
< 30 |
< 30 |
< 30 |
< 30 |
Total Dissolved Solids in ppm |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
PH |
6.5 - 8.5 |
6.5 - 8.5 |
6.5 - 8.5 |
6.5 - 8.5 |
6.5 - 8.5 |
In mixed-bed deionizers the cation-exchange and anion-exchange resins are intimately mixed and contained in a single pressure vessel. The thorough mixture of cation-exchangers and anion-exchangers in a single column makes a mixed-bed deionizer equivalent to a lengthy series of two-bed plants. As a result, the water quality obtained from a mixed-bed deionizer is appreciably higher than that produced by a two-bed plant.
Although more efficient in purifying the incoming feedwater, mixed-bed plants are more sensitive to impurities in the water supply and involve a more complicated regeneration process. Mixed-bed deionizers are normally used to ‘polish' the water to higher levels of purity after it has been initially treated by either a two-bed deionizer or a reverse osmosis unit.
Electrodeionization EDI Systems remove ions from aqueous streams, typically in conjunction with reverse osmosis (RO) and other purification devices. Our high-quality deionization modules continually produce ultrapure water up to 18.2MW/cm. EDI may be run continuously or intermittently
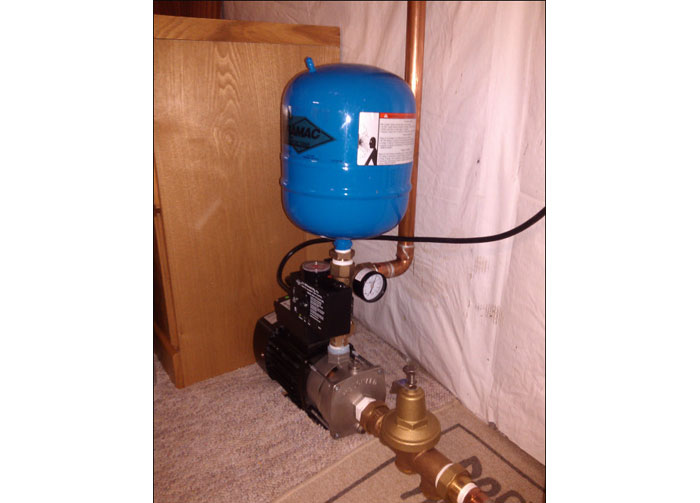
PRESSURE BOOSTING SYSTEM
AQUA LIFE GUARD RO System is a leading provider of deionization solutions. Our water deionizers are rugged, pre-engineered, pre-assembled, standardized units that minimize expensive installation and start-up costs. We have designed our Deionization systems to maximize the efficiency and repeatability of the unit during the service and regeneration modes

In the context of water purification, ion-exchange is a rapid and reversible process in which impurity ions present in the water are replaced by ions released by an ion-exchange resin. The impurity ions are taken up by the resin, which must be periodically regenerated to restore it to the original ionic form. (An ion is an atom or group of atoms with an electric charge. Positively-charged ions are called cations and are usually metals; negatively-charged ions are called anions and are usually non-metals).
The following ions are widely found in raw waters:
Ion Exchange ResinsThere are two basic types of resin - cation-exchange and anion-exchange resins. Cation exchange resins will release Hydrogen (H+) ions or other positively charged ions in exchange for impurity cations present in the water. Anion exchange resins will release hydroxyl (OH-) ions or other negatively charged ions in exchange for impurity anions present in the water.
The application of ion-exchange to water treatment and purification
There are three ways in which ion-exchange technology can be used in water treatment and purification: first, cation-exchange resins alone can be employed to soften water by base exchange; secondly, anion-exchange resins alone can be used for organic scavenging or nitrate removal; and thirdly, combinations of cation-exchange and anion-exchange resins can be used to remove virtually all the ionic impurities present in the feedwater, a process known as deionization. Water deionizers purification process results in water of exceptionally high quality.
DeionizationFor many laboratory and industrial applications, high-purity water which is essentially free from ionic contaminants is required. Water of this quality can be produced by deionization.
The two most common types of deionization are:
- Two-bed deionization
- Mixed-bed deionization
The two-bed deionizer consists of two vessels - one containing a cation-exchange resin in the hydrogen (H+) form and the other containing an anion resin in the hydroxyl (OH-) form. Water flows through the cation column, whereupon all the cations are exchanged for hydrogen ions. To keep the water electrically balanced, for every monovalent cation, e.g. Na+, one hydrogen ion is exchanged and for every divalent cation, e.g. Ca2+, or Mg2+, two hydrogen ions are exchanged. The same principle applies when considering anion-exchange. The decationised water then flows through the anion column. This time, all the negatively charged ions are exchanged for hydroxide ions which then combine with the hydrogen ions to form water (H2O).
|
Cations |
Anions |
|
Calcium (Ca2+) |
Chloride (Cl-) |
|
Magnesium (Mg2+) |
Bicarbonate (HCO3-) |
|
Sodium (Na+) |
Nitrate (NO3-) |
|
Potassium (K+) |
Carbonate (CO32-) |
|
Iron (Fe2+) |
Sulfate (SO42-) |
Technical Specifications: |
||||||
Model No. |
DM-10 |
DM-20 |
DM-30 |
DM-50 |
DM-65 |
|
Material of construction |
FRP |
FRP |
FRP |
FRP |
FRP |
|
Flow rate LPH |
Max |
100 |
200 |
600 |
1000 |
1500 |
Min |
10 |
20 |
60 |
100 |
150 |
|
Working Pressure Kg/CM2 |
Max |
2.5 |
2.5 |
2.5 |
2.5 |
2.5 |
Min |
0.5 |
1.5 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
Qty. of Ion exchange resin Lits. |
10 |
20 |
30 |
50 |
65 |
|
Output regeneration in Lits. |
200 |
600 |
1000 |
1750 |
2200 |
|
(Base on 1000 PPM IDS in Haw Water) |
||||||
Regenerate |
|||||
Commercial grade HCL |
Kg |
2.5 |
6 |
10 |
16 20 |
Caustic flakes (NaOH) |
Kg |
0.5 |
1.2 |
2.2 |
4.0 5.0 |
Treated Water Quality |
|||||
Electrical Conductivity Micromhos / Cm |
< 30 |
< 30 |
< 30 |
< 30 |
< 30 |
Total Dissolved Solids in ppm |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
PH |
6.5 - 8.5 |
6.5 - 8.5 |
6.5 - 8.5 |
6.5 - 8.5 |
6.5 - 8.5 |
In mixed-bed deionizers the cation-exchange and anion-exchange resins are intimately mixed and contained in a single pressure vessel. The thorough mixture of cation-exchangers and anion-exchangers in a single column makes a mixed-bed deionizer equivalent to a lengthy series of two-bed plants. As a result, the water quality obtained from a mixed-bed deionizer is appreciably higher than that produced by a two-bed plant.
Although more efficient in purifying the incoming feedwater, mixed-bed plants are more sensitive to impurities in the water supply and involve a more complicated regeneration process. Mixed-bed deionizers are normally used to ‘polish' the water to higher levels of purity after it has been initially treated by either a two-bed deionizer or a reverse osmosis unit.
Electrodeionization EDI Systems remove ions from aqueous streams, typically in conjunction with reverse osmosis (RO) and other purification devices. Our high-quality deionization modules continually produce ultrapure water up to 18.2MW/cm. EDI may be run continuously or intermittently
AQUA LIFE GUARD MODULER PEARL RO + Mineral
- Store the rainwater in containers above or above grounds or below grounds
- Recharge into soil for withdrawal later by ground water recharging basis.
- Rainwater can be stored in tanks
- Rainwater can be recharged into the ground.
Any rain water harvesting will have four elements :
- Catchments area
- Conduits
- Settlement Tank
- Recharge facility or storage facility.
The choice and effectiveness of any particular method is governed by local hydrological and soil conditions and ultimate use of water.
Methods of Rainwater Harvesting in Urban Cities.
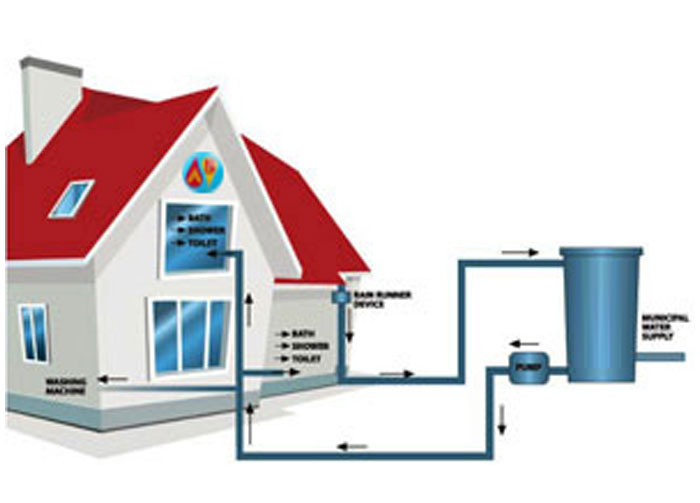

Need for Rain water harvesting :
Nature replenishes the ground water resources annually through rainfall by way of infiltration though soil layers. Due to urbanization, the soil surface exposed to natural recharge gets reduced. Therefore, natural recharge is diminishing, resulting in drying of wells. Ground water source has the benefit of availability where water is needed and during emergencies and scarcity period, the public at large or NGOs should take measure to improve the ground water recharge by rain water harvesting to maintain the reliable and sustainable ground water resource for supplementary domestic and industrial needs by ground water balance use.
Rain water Harvesting Aims and Objectives & Scope :
Rainwater harvesting may be defined as process of augmenting the natural infiltration of rainwater or surface run off into the ground by some artificial methods. The methods suggested are recharge through pits, trenches, bore wells shafts by directly diverting run off water into existing or disused wells or conserving the rain water by artificial storing and using the same for human use.
Catchments area :
The catchment is the area or surface, which receives rainfall directly. It can be any surface such as paved area like a terrace or courtyard of building or an unpaved area, like Lawn or open ground. Temporary structures like sloping sheds can also act as catchment. Run-off factor determines the quantity of water which will be available from the catchment run-off factors for wooded or grassy land is very less say 10% rest is absorbed by percolation, whereas run-off factor for paved or terraced area is 70 to 80% as most of the rainwater is available for recharge or storage except for water lost due to evaporation.
AQUA LIFE GUARD YOGA RO UV + UF
Are You?
Swimmer & Parent
Pool Owner, trustee & committee member
Pool Architect, consultant & specialist
Pool Builder & engineer
Pool Operator & maintenance staff
Swimming Coach, Trainer & Life Guard.
Environmentalist, NGO, corporate

What is the pool filtration technique, duration of filtration & backwash frequency ?
What is the filtration turnover time with respect to pool volume & depth?
Clarity of pool water & odor (freshness) from pool?
What is the permitted bather load per session with respect to pool surface area?
Is Chlorine & Chlorine derivatives used for pool water disinfection?
What is the Chlorine dose & free residual chlorine in the pool?
Ozonation used for swimming pool water treatment?
Importantly – Which standard/Guideline is followed for swimming pool water treatment.
Swimming pool water is contaminated by swimmers and environmental pollutants, which are in suspended & dissolved state
Sweat, Spitting, Nasal & pharyngeal products
Skin, hair, dandruffs
Skin Diseases & Infections
Cosmetics & Medications
Urine & Fecal matter
Bird droppings
Leaves & vegetationAlgae, Biomass,
Micro Insects, worms
Water-borne chemicals, foul/chemical odor
Dirt & Debris
Various types of bacteria and viruses can develop in the pool water making it un-safe for swimmers. Studies shows an adult swallow around 100 ml of pool water per swimming session & children swallow around 300 ml. The large water volumes involved, do not permit disposal of pool water.
Swimming pool water has therefore to be treated continually, to make it safe for swimmers.
This Involves
Filtration of suspended impurities
Disinfection of Water from micro-organisms & infections
Chemically Balancing of Ph, alkalinity, TDS, Disinfectant byproducts
Oxidize the organic impurities
Pools which are owned & used by single family occasionally with friends & relatives. Pool size can be from 20 m³ to 150 m³. Pools which are in the compound, back yard, basement, terrace, weekend bungalows, farm house etc. |
Pools having capacities from 150 m³ to 1,000 m³ liters are used by many swimmers at a time. |
Others which are daily used by members like sports clubs, recreational clubs, municipalities etc. Pools which are used for local, national & international competitions are of Semi-Olympic & Olympic size. These pools are from 1,200 m³ to 6,000 m³ |
Pool Water Filtration & Ozonation Plant
It makes pool water very safe for swimmers & especially children. Research shows that most people & children intake around 100 – 300 ml of water, while swimming. The technology used to make swimmers free from skin rashes, eye rending, hair fall, cloudy appearance of the pool water, foul & chemical odor
Products
We provide comprehensive range of swimming pool water treatment equipments & plants. These products are durable & efficient to treat pool water according to the design & client’s requirements.
The components uses for swimming pool water treatment are manufactured by companies which are among industry leaders. Most of these brands are well certified by top certifying agencies
We offer wide range of pool water filters, ozonators & U.V. purifiers that can be custom designed as per the international guidelines / specification of our customers.
Swimming Pool Pressure Sand Filter Selection Guide :
Swimming pool pressure sand filter vessel are selected from swimming pool volume, desired turnover time & filtration velocity.
Turnover* time is the time taken by recirculation pump to turnover the entire pool volume. (Lower turnover time better is the pool water clarity, quality & disinfection level).
Filtration velocity decides the filtration degree / filtration efficiency. (Lower filter velocity is better)
Pressure Sand Filters :
Pressure Sand Filter Are available in different material of constructions, with automatic /semi-automatic & PLC based fully automatic operations like service, back-wash, rinse etc.
Glass-fiber reinforced Plastic (GFRP) :
GFRP vessels are very long lasting & corrosion resistance.
Private Swimming Pool Pressure Sand Filters : FRP Series
Swimming pools are classified as :
Private: Public : Competition / Diving Pools :
